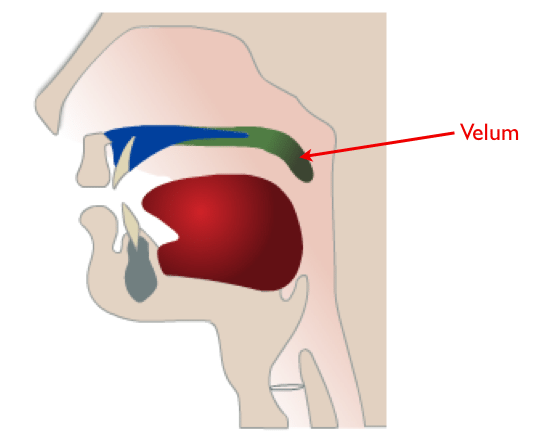
The function of the levator veli palatini muscle is to retract and elevate the velum. As this muscle contracts during speech, it pulls the velum up at a 45-degree angle to close against the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Furthermore, Does the velum move?
How many Foramina are there in total on the palate? It consists of two main parts; the hard palate and soft palate.
…
Palate.
| Structure | Bony anterior two-thirds: maxillae and palatine bones Muscular posterior one-third: tensor veli palatini, levator veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus and musculus uvulae |
|---|---|
| Foramina | Incisive fossa, greater and lesser palatine foramina |
Besides, What causes the nasopharynx not to close properly? Causes include a history of cleft palate, adenoidectomy, irregular adenoids, cervical spine anomalies, or oral/pharyngeal tumor removal. In contrast, « velopharyngeal incompetence » refers to a neurogenic cause of inadequate velopharyngeal closure.
Contenus
What 2 bones make up the hard palate?
The hard palate comprises about two-thirds of the total palate surface area, and its underlying bony structure consists of the palatine processes of the maxilla and the horizontal plates of the palatine bones.
also, Is velum raised for vowels? Similarly, in oral vowels, the velum is regularly higher for high vowels and lower for low vowels [2], [3]. Though the velic port is still closed (no nasal airflow) in both contexts, it still shows a regular difference in position; despite this regularity, velum height is not a contrastive feature for vowel production.
How does the velum close? Figure 3 shows how the velum closes against the back wall of the throat during speech. The side walls close against the velum so that all of these structures come together as a valve. When the velopharyngeal valve closes, the air and sound are sent into the mouth for speech.
How does the velum open and close? This is a necessary function as most speech sounds are non-nasal. If we didn’t have the velum closing off the nasal cavity, we would all be talking through our noses, which would not be pleasant to listen to or produce. The velum does open for three consonant sounds – the nasal sounds /m/ /n/ and /ng/.
What is incisive canal?
The incisive canal, also known as the nasopalatine canal, is an interosseous conduit through the anterior maxilla connecting the oral and nasal cavities. Within this canal lies the nasopalatine nerve and the vascular anastomosis between the greater palatine and sphenopalatine arteries.
Where is sphenoid? An unpaired bone located in the cranium (or skull), the sphenoid bone, also known as the “wasp bone,” is located in the middle and toward the front of the skull, just in front of the occipital bone.
What is magnum foramen?
The foramen magnum is the largest foramen of the skull. It is located in the most inferior portion of the cranial fossa as a part of the occipital bone.
How do you know if you have nasopharyngeal? Symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer
a lump in the neck that doesn’t go away after 3 weeks. hearing loss (usually only in 1 ear) tinnitus (hearing sounds that come from inside the body rather than from an outside source) a blocked or stuffy nose (usually only blocked on 1 side)
What is Stage 3 nasopharyngeal?
Stage 3 nasopharyngeal cancer means one of the following: The cancer has spread to nearby bones and air cavities (sinuses). It might also have spread to lymph nodes on one or both sides of the neck, or behind the throat, but not anywhere else. The affected lymph nodes are not more than 6 cm across.
Can food get stuck in nasopharynx?
However, an ingested foreign body getting lodged in the nasopharynx is even more rare with only a handful of reported cases (4). These mostly result from naïve attempts at removal by the parents, primary-care physicians (5), or quacks.
What bones are unpaired? The unpaired bones are the vomer and mandible bones. Although classified with the brain-case bones, the ethmoid bone also contributes to the nasal septum and the walls of the nasal cavity and orbit.
What bones form the cheekbone? The zygomatic bone forms the bony prominence of the cheek. It also forms the lower lateral part of the orbital margin, and this part of the lateral orbital wall. The zygomatic bone extends backward to meet the zygomatic process of the temporal bone, forming the zygomatic arch.
More from Foodly tips!
What is upper part of mouth called?
The roof of the mouth. The front portion is bony (hard palate), and the back portion is muscular (soft palate).
How do I increase my velum?
What is a lowered velum?
If the velum is lowered, we can articulate either nasal sounds, if the air is expelled exclusively via the nasal cavity, or nasalized sounds if, in spite of the lowered position of the velum, the air is still allowed to go out through the mouth as well as through the nose.
How do you know if velum is raised or lowered? The pendulous tip is the uvula. During respiration and production of nasal sounds the velum is lowered. When you say “ah” you can see the velum raise. During oral sounds or activities such as sucking or blowing, the velum is raised.
Help Foodly.tn team, don’t forget to share this post !