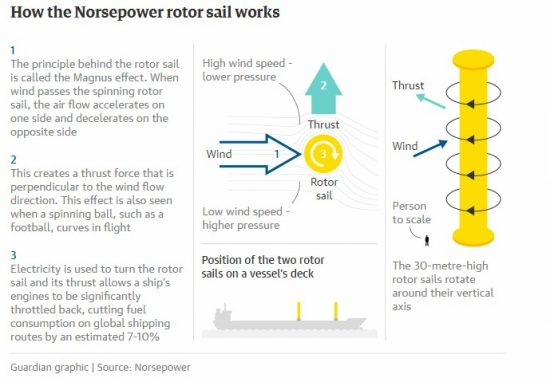
The Norsepower Rotor Sail technology is around ten times more efficient than a conventional sail, because more lift is produced with a much smaller sail area. Due to its simplicity, it requires no reefing or crew attention when in operation. It is « push-button wind propulsion » from the bridge.
Then, How do boat rotors work?
What is tilting rotor sails? Newbuild Bulk Carrier to Get Tilting ‘Rotor Sails’
In favorable wind conditions, the vessel will be able to maintain its regular service speed by sail alone, according to Norsepower. The tilting feature, a first, allows the SC Connector to navigate height restricted routes while in operation in the North Sea market.
Moreover, How does a Turbosail work? A movable, flap-like trailing-edge shutter and a fan-drawn aspiration system are used for control and increase the magnitude of the maximum reaction force. As a result of this design, the turbosail provides a reaction force, a component of which, thrust, is available for the direction of travel.
Contenus
What is the spinning thing on yachts?
Propeller – A rotating device with blades designed to move a boat forward or backward through the water.
also, How efficient are rotor sails? The rotor sail is said to be 10 times more efficient than a conventional sail, creating more lift with a smaller surface area. However, like conventional sails, it depends on the direction of the wind, so is best used as an auxiliary propulsion system to supplement a typical fuel-powered vessel.
What is Magnus effect propulsion? The Magnus effect is an interesting thing, where fluid flowing over a rotating object generates an aerodynamic force at a right angle to the direction of the flow and the axis of rotation. (It’s why curveballs curve.) This can be used for propulsion on a boat, by spinning a tall cylinder called a Flettner rotor.
How do you get the Magnus effect on a plane?
What are the parts of a ship called?
E.g. rudder, anchor, bow, keel, accommodation, propeller, mast, bridge, hatch coves and bow thrusters are some common visible parts. In contrast, bulkheads, frames, cargo holds, hopper tank, double bottom, girders, cofferdams, side shell etc., are the invisible parts of a ship.
What happened to the ship the Calypso? Calypso was involved in a mooring accident and sank in the harbour of Singapore in 1996. Captain Cousteau decided then that the vessel must be saved and arranged to have her transported back to France.
What is the name of Jacques Cousteau’s famous Turbo sailing ship?
Alcyone was created as an expedition ship and to test the operation of a new kind of marine propulsion system, the turbosail. Alcyone’s two turbosails augment its diesel engines. Since the accidental sinking of Calypso, Alcyone has been the Cousteau Society’s expedition vessel.
Why do cruise ships not rock? Cruise ship stabilisers can eliminate about 85% of the roll (the side to side rocking motion), but unfortunately they do nothing to elimiate pitching (the up and down motion). To counter this, cruise ships are designed with a long narrow bow to cut through the waves rather than climb them.
What are the white balls on top of yachts?
The big white balls on top of cruise ships are Radomes. A Radome is made up of two parts, a Radar and a Dome, hence the name Ra-dome. The dome covers the radar equipment protecting it from the weather and hiding it from guests. A radome can also include satelitte equipment.
Why do marine radars spin?
The spinning radar on a boat is a unit that usually sits at the highest part of the structure. It scans the horizon to pick up any radiomagnetic signals from objects within range over a 360-degree pattern.
Why do cruise ships not use sails?
Who invented sails for boats? The exact timing is unknown, but archaeologists do know that at some point in the 1st century CE, the Greeks began using sails that allowed for tacking and jibing—technological advancements that are believed to have been introduced to them by Persian or Arabic sailors.
More from Foodly tips!
How does spin affect the trajectory of a ball?
(a) Force due to spin
A spinning ball sets the air around it in motion in a thin layer near the surface of the ball. The flow of air around the ball is altered in such a way that the air pressure on top of a spin- ning ball is decreased if the ball has topspin and is increased if the ball has backspin.
Does the Magnus effect create lift? It’s that pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of a wing that generates the lift that keeps an aircraft aloft. But there’s another way to generate lift, he notes. This alternative is known as the Magnus effect. It develops when air flows past a rotating sphere or cylinder, Rylan explains.
Why is the Magnus effect important?
Named after the German physicist and chemist H.G. Magnus, who first (1853) experimentally investigated the effect, it is responsible for the “curve” of a served tennis ball or a driven golf ball and affects the trajectory of a spinning artillery shell.
Where is the Magnus effect used? The most readily observable case of the Magnus effect is when a spinning sphere (or cylinder) curves away from the arc it would follow if it were not spinning. It is often used by association football and volleyball players, baseball pitchers, and cricket bowlers.
Help Foodly.tn team, don’t forget to share this post !