Similarly, in oral vowels, the velum is regularly higher for high vowels and lower for low vowels [2], [3]. Though the velic port is still closed (no nasal airflow) in both contexts, it still shows a regular difference in position; despite this regularity, velum height is not a contrastive feature for vowel production.
Furthermore, What sounds are classified velum? Velar: Velar sounds are made when the back of the tongue (tongue dorsum) raises towards the soft palate, which is located at the back of the roof of the mouth. This soft palate is known as the velum. An effective constriction is then formed when these two articulators come into contact with each other.
Is the velum raised for G? During speech tasks the velum also elevates and retracts to separate the oral cavity (mouth) from the nasal cavity to produce consonants including /p, b, t, d, k, g, s, z, ch, zh, sh, r, l/ and remains open for nasal sounds /m,n,ng/.
Besides, Which phonemes require an open velum? The velum does open for three consonant sounds – the nasal sounds /m/ /n/ and /ng/.
Contenus
How do you tell if velum is up or down?
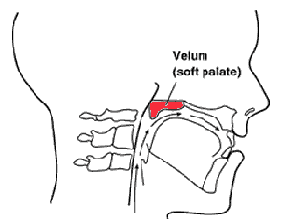
also, What is velum linguistics? The palate is generally defined as the roof of the oral cavity and separates the nasal and oral cavities from one another. It is divided into a region with underlying bone called the hard palate and a region made up of connective tissue and muscle called or soft palate, or velum.
What is the position of velum? soft palate, also called palatal velum, velum, or muscular palate, in mammals, structure consisting of muscle and connective tissue that forms the roof of the posterior (rear) portion of the oral cavity.
Where is the velum? The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate.
What happens when the velum is closed?
A person’s speaking voice takes on a nasal tone when too much air flows through the nose. This happens when the moving tissue at the back of the roof of the mouth, called the soft palate or the velum, fails to close an opening called the velophayngeal port. The result is called velopharyngeal dysfunction (VPD).
Is the velum an active articulator? Velum Listed as Passive and Active Articulator.
Is the uvula part of the velum?
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate.
…
| Soft palate | |
|---|---|
| FMA | 55021 |
| Anatomical terminology |
What is a velum in cnidarians? (biology) A covering or partition of thin membranous tissue, such as the veil of a mushroom, a rim of tissue around the margin of the bell of certain cnidarians, or a membrane of the brain.
What are the three main articulators?
The main articulators are the tongue, the upper lip, the lower lip, the upper teeth, the upper gum ridge (alveolar ridge), the hard palate, the velum (soft palate), the uvula (free-hanging end of the soft palate), the pharyngeal wall, and the glottis (space between the vocal cords).
What is the function of nasopharynx?
The main function of your nasopharynx is to connect your nasal passages to the rest of your respiratory system. This allows air to get from your nose to your lungs. Your nasopharynx also helps: Control pressure between your nasopharynx and middle ear.
What are the 7 organs of speech? Speech organs include the lips, teeth, tongue, palate, uvula, nasal and oral cavities, and vocal cords, as located in Figure 2.
What is the velum in real life? The design of the JoBuilt Velum is based on a real life Piper PA-46, SOCATA TBM.
More from Foodly tips!
Which cranial nerve Innervates the velum?
The tensor veli palatini is innervated by the mandibular nerve.
Is the velum and uvula the same? As nouns the difference between velum and uvula
is that velum is a thin membrane, resembling a veil, such as: while uvula is (anatomy) the fleshy appendage that hangs from the back of the palate, that closes the nasopharynx during swallowing.
What does the velum do during swallowing?
The palatopharyngeus and tensor veli palatini muscles produce the tension of the soft palate during swallowing. This enables the tongue to press against the soft palate and push the food towards the oropharynx.
How do you test for nasality? Hold mirror under nares to detect nasal air emission—look for fogging during production of voiceless oral pressure consonants. Listen for sound/airflow exiting the nostril by placing one end of a straw or listening tube at nostril entrance and the other end to the examiner’s ear.
What is velar insufficiency?
Velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI) is when the soft palate does not close tightly against the back of the throat, leading to air coming out the nose (characterized by hypernasality and/or nasal air emission) during speech. This can cause speech that is difficult to understand.
Is the basic unit of phonetics? Phonology refers to the sound system of a language. In general, the basic unit of phonology is the phoneme, which is an individual speech sound (such as /p/) that can often be represented by a single grapheme, or letter (such as the letter p).
What is the difference between manner and place of articulation?
The manner of articulation refers to the way the articulators are set so that the resonance effect is possible. The place of articulation is the description of the place where the obstruction in the vocal tract takes place.
What does the phonetic symbol D represent?
| Symbol | Phonetic value | Example |
|---|---|---|
| d | voiced alveolar stop | dad |
| ḏ | palatalized [dʸ]; can be pronounced [ǰ] | Egyptian |
| or spirantized [d], same as [ð] | Ancient Hebrew | |
| ḍ | voiced retroflex stop; IPA [ɖ] | Indic |
Help Foodly.tn team, don’t forget to share this post !