The palate is generally defined as the roof of the oral cavity and separates the nasal and oral cavities from one another. It is divided into a region with underlying bone called the hard palate and a region made up of connective tissue and muscle called or soft palate, or velum.
Furthermore, Is velum raised for vowels? Similarly, in oral vowels, the velum is regularly higher for high vowels and lower for low vowels [2], [3]. Though the velic port is still closed (no nasal airflow) in both contexts, it still shows a regular difference in position; despite this regularity, velum height is not a contrastive feature for vowel production.
What is velum botany? velum (plural vela or velums) a thin membrane resembling a veil or curtain, such as: (anatomy) the soft palate. (botany) a thin membrane partially covering the cluster of sporangia near the leaf base in quillworts and their extinct relatives.
Besides, Does the velum move?
Contenus
Is the uvula part of the velum?
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate.
…
| Soft palate | |
|---|---|
| FMA | 55021 |
| Anatomical terminology |
also, How do I increase my velum?
What is a velum in cnidarians? (biology) A covering or partition of thin membranous tissue, such as the veil of a mushroom, a rim of tissue around the margin of the bell of certain cnidarians, or a membrane of the brain.
Is velum an organ? Zoology A ciliated swimming and feeding organ that develops in certain larval stages of most gastropod and bivalve mollusks.
What is the meaning of FOWN?
1 : a young deer especially : one still unweaned or retaining a distinctive baby coat. 2 : kid sense 2. 3 : a light grayish brown.
How does the velum open and close? This is a necessary function as most speech sounds are non-nasal. If we didn’t have the velum closing off the nasal cavity, we would all be talking through our noses, which would not be pleasant to listen to or produce. The velum does open for three consonant sounds – the nasal sounds /m/ /n/ and /ng/.
How does the velum close?
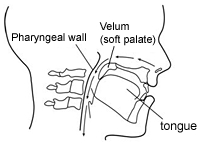
Figure 3 shows how the velum closes against the back wall of the throat during speech. The side walls close against the velum so that all of these structures come together as a valve. When the velopharyngeal valve closes, the air and sound are sent into the mouth for speech.
What muscle lowers the velum? The palatoglossus arises from the anterior surface of the soft palate and inserts into the lateral aspect of the tongue base. Innervated by the pharyngeal plexus, it simultaneously lowers the velum and elevates the tongue upwards and backwards. It depresses the palate for nasal speech.
Where is Laryngopharynx located?
Where is the Laryngopharynx located? Posterior to the larynx, from the superior border of the epiglottis and pharynx-epiglottis folds to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage.
Where is the pharynx located?
The pharynx is a hollow tube that starts behind the nose, goes down the neck, and ends at the top of the trachea and esophagus. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx.
How do you fix a collapsed soft palate? The Pillar procedure, also called palatal restoration, is a limited-access treatment for mild to moderate OSA. The procedure involves implanting 3 small, polyester-woven rods in the soft palate. The rods work like a scaffold to stiffen the soft palate and stop it from collapsing into your airway.
How do you lift your uvula?
More from Foodly tips!
What is a dropped palate?
Isolated palatal collapse was defined as collapse at the level of palate without any involvement of other airway structures. When more than one structure was involved in obstruction, the structure collapsing at the least negative pharyngeal pressure was considered predominant.
What do the cnidocytes do? Cnidocytes (‘stinging cells’) are specialized cells that define the phylum Cnidaria (sea anemones, jellyfish, corals and hydras). They contain an “explosive” organelle called cnidocyst that acts as a 600 million-years-old microscopic injection system and is important for prey capture and anti-predator defense.
What is the function of cnidocytes in cnidarians?
Cnidarians contain specialized cells known as cnidocytes (“stinging cells”) containing organelles called nematocysts (stingers). These cells are present around the mouth and tentacles, and serve to immobilize prey with toxins contained within the cells.
Are polyps motile? Polyp forms are sessile as adults, with a single opening (the mouth/anus) to the digestive cavity facing up with tentacles surrounding it. Medusa forms are motile, with the mouth and tentacles hanging down from an umbrella-shaped bell.
Help Foodly.tn team, don’t forget to share this post !